Riemann hypothesis
sabato, Ottobre 30th, 2021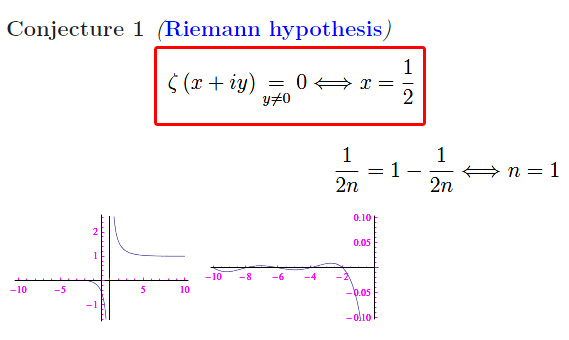
As is well known the Riemann Zeta Function, is function of complex variable s=x+iy defined by the sum of the following Dirichlet series:
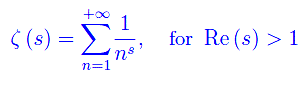
However, the function can be defined by holomorphic extension in all C excluding the polar singularity in s=1. More precisely, the holomorphic extension gives rise to the following functional equation:
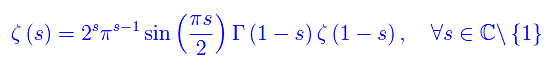
From a property of the Dirichlet series that defines the zeta function, it follows the non-existence of zeros for Re(s) > 1, and from the functional equation it follows the non-existence of zeros with non-zero imaginary part for Re(s) < 0. On the other hand, for Re(s) < 0 there are zeros with a null imaginary part (trivial zeros). They are given by (fig. 1)
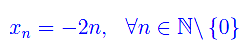
by the following property (see Edwards)
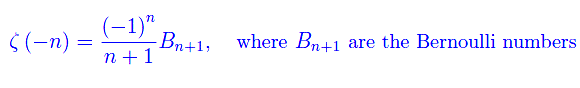
Conversely, zeros with non-zero imaginary part are called non-trivial zeros.
(altro…)


 Congettura di Riemann
Congettura di Riemann Trasformata discreta di Fourier
Trasformata discreta di Fourier
 Trasformata di Fourier nel senso delle distribuzioni
Trasformata di Fourier nel senso delle distribuzioni Trasformata di Fourier
Trasformata di Fourier  Infinitesimi ed infiniti
Infinitesimi ed infiniti Limiti notevoli
Limiti notevoli Punti di discontinuità
Punti di discontinuità Misura di Peano Jordan
Misura di Peano Jordan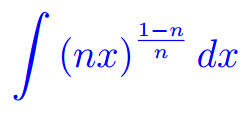 Eserciziario sugli integrali
Eserciziario sugli integrali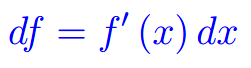 Differenziabilità
Differenziabilità 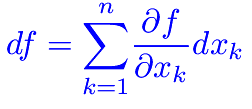 Differenziabilità (2)
Differenziabilità (2)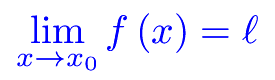 Esercizi sui limiti
Esercizi sui limiti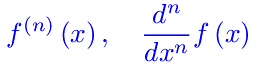 Appunti sulle derivate
Appunti sulle derivate Studio della funzione
Studio della funzione Esercizi sugli integrali indefiniti
Esercizi sugli integrali indefiniti Algebra lineare
Algebra lineare Analisi Matematica 2
Analisi Matematica 2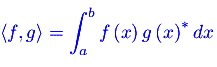 Analisi funzionale
Analisi funzionale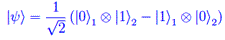 Entanglement quantistico
Entanglement quantistico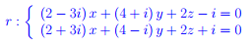 Spazio complesso
Spazio complesso Biliardo di Novikov
Biliardo di Novikov Intro alla Meccanica quantistica
Intro alla Meccanica quantistica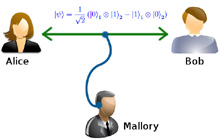 Entanglement Quantistico
Entanglement Quantistico